In the computer security context, a hacker is someone who seeks
and exploits weaknesses in a computer system or computer network. Hackers may be motivated by a multitude of reasons, such as profit, protest, or challenge. The subculture that has evolved around hackers is often referred to as the computer underground and is now a known community. While other uses of the word hacker exist that are not related to computer security, such as referring to someone with an advanced understanding of computers and computer networks, they are rarely used in mainstream context. They are subject to the long standing hacker definition controversy about the true meaning of the term hacker. In this controversy, the term hacker is reclaimed bycomputer programmers who argue that someone breaking into computers is better called a cracker, not making a difference between computer criminals (black hats) and computer security experts (white hats). Some white hat hackers claim that they also deserve the title hacker, and that only black hats should be called crackers.
Classifications
Several subgroups of the computer underground with different attitudes use different terms to demarcate themselves from each other, or try to exclude some specific group with which they do not agree.
Eric S. Raymond (author of The New Hacker's Dictionary) advocates that members of the computer underground should be called crackers. Yet, those people see themselves as hackers and even try to include the views of Raymond in what they see as one wider hacker culture, a view harshly rejected by Raymond himself. Instead of a hacker/cracker dichotomy, they give more emphasis to a spectrum of different categories, such as white hat, grey hat, black hat and script kiddie. In contrast to Raymond, they usually reserve the term cracker for more malicious activity.
According to Ralph D. Clifford, a cracker or cracking is to "gain unauthorized access to a computer in order to commit another crime such as destroying information contained in that system".These subgroups may also be defined by the legal status of their activities.
1.White hat
A white hat hacker breaks security for non-malicious reasons, perhaps to test their own security system or while working for a security company which makes security software. The term "white hat" in Internet slang refers to an ethical hacker. This classification also includes individuals who perform penetration tests and vulnerability assessments within a contractual agreement. The EC-Council, also known as the International Council of Electronic Commerce Consultants, is one of those organizations that have developed certifications, course-ware, classes, and online training covering the diverse arena of Ethical Hacking.
2.Black hat
A "black hat" hacker is a hacker who "violates computer security for little reason beyond maliciousness or for personal gain" (Moore, 2005). Black hat hackers form the stereotypical, illegal hacking groups often portrayed in popular culture, and are "the epitome of all that the public fears in a computer criminal". Black hat hackers break into secure networks to destroy data or make the network unusable for those who are authorized to use the network. Black hat hackers also are referred to as the "crackers" within the security industry and by modern programmers. Crackers keep the awareness of the vulnerabilities to themselves and do not notify the general public or manufacturer for patches to be applied. Individual freedom and accessibility is promoted over privacy and security. Once they have gained control over a system, they may apply patches or fixes to the system only to keep their reigning control. Richard Stallman invented the definition to express the maliciousness of a criminal hacker versus a white hat hacker that performs hacking duties to identify places to repair.
3.Grey hat
A grey hat hacker is a combination of a black hat and a white hat hacker. A grey hat hacker may surf the internet and hack into a computer system for the sole purpose of notifying the administrator that their system has a security defect, for example. Then they may offer to correct the defect for a fee.
4.Elite hacker
A social status among hackers, elite is used to describe the most skilled. Newly discovered exploits will circulate among these hackers. Elite groups such as Masters of Deception conferred a kind of credibility on their members.
5.Script kiddie
A script kiddie (also known as a skid or skiddie) is a non-expert who breaks into computer systems by using pre-packaged automated tools written by others, usually with little understanding of the underlying concept—hence the term script (i.e. a prearranged plan or set of activities) kiddie (i.e. kid, child—an individual lacking knowledge and experience, immature).
6.Neophyte
A neophyte, "n00b", or "newbie" is someone who is new to hacking or phreaking and has almost no knowledge or experience of the workings of technology, and hacking.
7.Blue hat
A blue hat hacker is someone outside computer security consulting firms who is used to bug test a system prior to its launch, looking for exploits so they can be closed. Microsoft also uses the term BlueHat to represent a series of security briefing events.
8.Security exploits
A security exploit is a prepared application that takes advantage of a known weakness. Common examples of security exploits are SQL injection,Cross Site Scripting and Cross Site Request Forgery which abuse security holes that may result from substandard programming practice. Other exploits would be able to be used through FTP, HTTP, PHP, SSH, Telnet and some web-pages. These are very common in website/domain hacking.
Techniques:-
- Vulnerability scanner
- A vulnerability scanner is a tool used to quickly check computers on a network for known weaknesses. Hackers also commonly use port scanners. These check to see which ports on a specified computer are "open" or available to access the computer, and sometimes will detect what program or service is listening on that port, and its version number. (Note that firewallsdefend computers from intruders by limiting access to ports/machines both inbound and outbound, but can still be circumvented.)
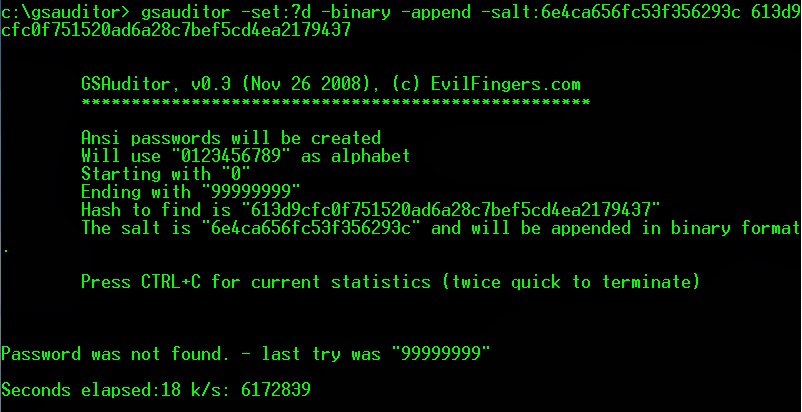
- Password cracking
- Password cracking is the process of recovering passwords from data that has been stored in or transmitted by a computer system. A common approach is to repeatedly try guesses for the password.
- Packet sniffer
- A packet sniffer is an application that captures data packets, which can be used to capture passwords and other data in transit over the network.
- Spoofing attack (Phishing)
- A spoofing attack involves one program, system, or website successfully masquerading as another by falsifying data and thereby being treated as a trusted system by a user or another program. The purpose of this is usually to fool programs, systems, or users into revealing confidential information, such as user names and passwords, to the attacker.
- Rootkit
- A rootkit is designed to conceal the compromise of a computer's security, and can represent any of a set of programs which work to subvert control of an operating system from its legitimate operators. Usually, a rootkit will obscure its installation and attempt to prevent its removal through a subversion of standard system security. Rootkits may include replacements for system binaries so that it becomes impossible for the legitimate user to detect the presence of the intruder on the system by looking at process tables.
- Social engineering
- When a hacker, typically a black hat, is in the second stage of the targeting process, he or she will typically use some social engineering tactics to get enough information to access the network. A common practice for hackers who use this technique, is to contact the system administrator and play the role of a user who cannot get access to his or her system. An example of this technique is contained in the beginning of the 1995 film Hackers, in which the protagonist Dade "Zero Cool" Murphy makes a phone call to a somewhat clueless employee in charge of security at a TV network company, and then tricks the employee into giving him the modem's phone number by posing, convincingly, as a top-notch accountant who also works for the same company.
- Hackers who use this technique have to be quite savvy and choose the words they use carefully, in order to trick the system administrator into giving them information. In some cases only an employed help desk user will answer the phone and they are generally easy to trick. Another typical hacker approach is for the hacker to act like a very angry supervisor and when his/her authority is questioned they will threaten the help desk user with their job. Social engineering is very effective because users are the most vulnerable part of an organization. All the security devices and programs in the world won't keep an organization safe if an employee gives away a password. Black hat hackers take advantage of this fact. Social engineering can also be broken down into four sub-groups. These are intimidation, helpfulness, technical, and name-dropping:
- Intimidation As stated above, with the angry supervisor, the hacker attacks the person who answers the phone with threats to their job. Many people at this point will accept that the hacker is a supervisor and give them the needed information.
- Helpfulness Opposite to intimidation, helpfulness is taking advantage of a person's natural instinct to help someone with a problem. The hacker will not get angry and instead act very distressed and concerned. The help desk is the most vulnerable to this type of social engineering, because it generally has the authority to change or reset passwords, which is exactly what the hacker needs.
- Name-dropping Simply put, the hacker uses the names of advanced users as "key words", and gets the person who answers the phone to believe that they are part of the company because of this. Some information, like web page ownership, can be obtained easily on the web. Other information such as president and vice president names might have to be obtained via dumpster diving.
- Technical Using technology is also a way to get information. A hacker can send a fax or an email to a legitimate user in hopes to get a response containing vital information. Many times the hacker will act like he/she is involved with law enforcement and needs certain data for record keeping purposes or investigations.
- Trojan horses
- A Trojan horse is a program which seems to be doing one thing, but is actually doing another. A trojan horse can be used to set up a back door in a computer system such that the intruder can gain access later. (The name refers to the horse from the Trojan War, with the conceptually similar function of deceiving defenders into bringing an intruder inside.)
- Computer virus
- A virus is a self-replicating program that spreads by inserting copies of itself into other executable code or documents. Therefore, a computer virus behaves in a way similar to a biological virus, which spreads by inserting itself into living cells.
- While some are harmless or mere hoaxes, most computer viruses are considered malicious.
- Computer worm
- Like a virus, a worm is also a self-replicating program. A worm differs from a virus in that it propagates through computer networks without user intervention. Unlike a virus, it does not need to attach itself to an existing program. Many people conflate the terms "virus" and "worm", using them both to describe any self-propagating program.
- Key loggers
- A key logger is a tool designed to record ("log") every keystroke on an affected machine for later retrieval. Its purpose is usually to allow the user of this tool to gain access to confidential information typed on the affected machine, such as a user's password or other private data. Some key loggers use virus-, trojan-, and rootkit-like methods to remain active and hidden. However, some key loggers are used in legitimate ways and sometimes to even enhance computer security. As an example, a business might have a key logger on a computer used at a point of sale and data collected by the key logger could be used for catching employee fraud.
Tools and Procedures
- A thorough examination of tools, uses and procedures may be found in the Course workbook by Cengage Learning as part of the E|CSA certification knowledge-base.
 Thank you for Reading Hope you Like it :-
Thank you for Reading Hope you Like it :-- Connect Me on Facebook Click Here






























ReplyDeleteHello everyone, i would like to share my experience with you all, I lost over 100 thousand dollars to all these fake so called BO merchants , after several attempts in trying to recover my money all efforts failed, i was looking through the page of the internet then i saw cybergoldenhacker they were recommended as a good and reputable company so i reach out to them, to my surprise i was able to to recover all my funds
contact: cybergoldenhacker at gmail dot com